Table of Contents
GST Login and Registration Process
GST Login Portal helps you to manage your GST (Goods and Services tax) online.
Taxes can be a confusing thing to understand. This is especially true for filling out or submitting GST forms. But you don’t need to worry, it is a very simple process.
In this article, we’ll explain everything about GST. We’ll do it in a simple way that’s easy to understand. So, you’ll have a clear idea of how it works and what you need to have access to the GST login Portal.
What is GST and GST Login Portal?
In India, GST stands for Goods and Services Tax. It is important in the world of taxes. But what exactly is GST, and why does it matter? Let’s Understand this in detail.
GST is a type of tax that replaces several other taxes like VAT, service tax, and more. It’s like a one-stop tax for all goods and services across the Country.
This applies when you buy groceries, clothes, or get a haircut. GST is there.
Now, why is GST important? Well, for starters, it makes things simpler. Before GST, there were many taxes for different items. They confused businesses and customers.
But now, with GST, it’s easier to understand and manage taxes.
Here’s how it works. When you buy something, like a shirt, the shopkeeper includes GST in the price. This GST then goes to the government. Like when a business sells a service, like repairing a phone, GST applies there too.
GST is divided into different slabs based on the type of goods or services. Some items have a higher GST rate, while others have a lower one. For example, rice and vegetables are items you need every day.
But GST isn’t about collecting taxes; it’s also about making things fairer. With the GST Login Portal, businesses can claim credits for the GST they pay on their purchases. This means they don’t end up paying taxes on taxes.
Another important aspect of GST is compliance. Businesses need to register for the GST Login Portal. They also must file regular returns. These returns detail their sales and purchases. This helps the government track tax payments. It ensures the system is transparent.
Read also: – How to Add Nomination in EPF Account.
How to Register for the GST Login Portal?
Registering for Goods and Services Tax (GST) might seem hard. But, it is simple. However, all businesses must register for the GST Login Portal. Those with a turnover above a certain threshold (Rs) need it. 40 lakhs for goods and Rs. 20 lakhs for services). Below is the guide that will help you throughout the process:
Check Eligibility – First, check if your business meets the criteria for GST registration. If Any business exceeds the annual turnover of Rs. 40 lakhs (Rs. 10 Lakhs for Northeastern states) needs to register under GST.
Arrange Documents – Next, get all the needed documents. You need them for registration. These include the PAN card and Aadhaar card. Also, you need proof of business registration.
- Access the GST Portal – Go to the official GST portal (www.gst.gov.in) for GST registration. Click “Services” and select “Registration” from the menu.
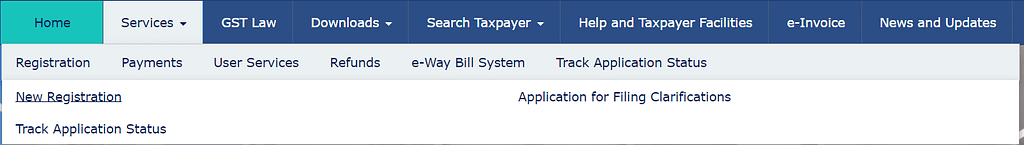
- Fill out the Form – Fill out the GST registration form. Use accurate information. Check all the details again before submitting. This will avoid errors.

- Verification – Once you fill out the form, you will receive an OTP (One-Time-Password) on your registered mobile number.
- Submit Documents – Upload the required documents. Follow the guidelines on the portal. Make sure all documents are clear. They should be easy to read. It will help you to speed up the process.
- ARN Generation – After you submit, you’ll get an Application Reference Number (ARN). You’ll get it via email and SMS. You can use this ARN to track the status of your application.
- Verification and Approval – The GST department will check the details of your application. Once verified, you’ll get your GSTIN. You’ll also get a GST certificate.
Congratulations! You’re now a GST-registered taxpayer. This GST login Portal lets you run your business without any hassle in the Indian market.
How to do GST Login?
Are you a business owner in India wanting to access the GST Login portal but don’t know how? You do not need to worry, it’s an easy process! The GST Login portal is your gateway.
You can use it to manage your Goods and Services Tax tasks online. Here’s a simple guide to help you login:
- Visit the GST Login Portal – Open your web browser and type www.gst.gov.in in the address bar. This will take you to the official GST portal.
- Click on “Login” – Once on the GST portal’s homepage, locate and click on the “Login” button. It’s usually positioned at the top right corner of the page.

- Enter Credentials – When you reach the GST login Portal page, you will see a prompt. You need to provide your username and password. Your username is usually your GSTIN. Or, it’s the email you used during registration.
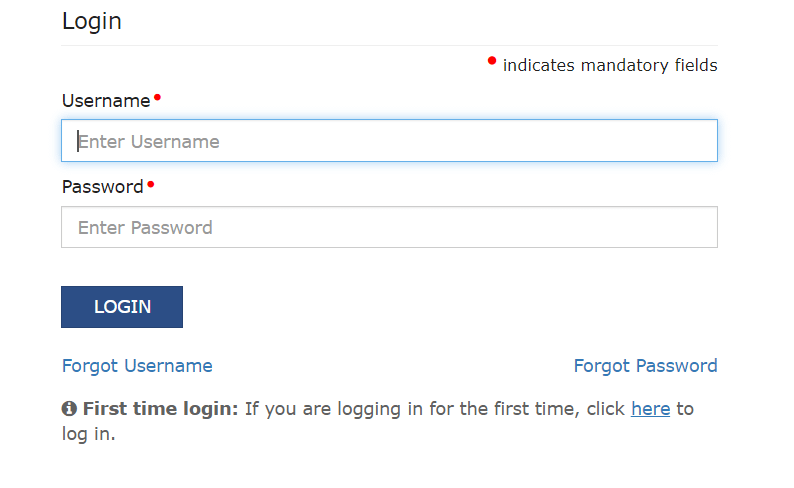
- Click “Login” – Enter your username and password. Then, click the “Login” button to proceed. Check your credentials. Make sure they are accurate.
- Complete CAPTCHA (if prompted) – In some cases, you may need to complete a CAPTCHA verification to prove you are not a robot. Follow the instructions provided. Use them to complete the verification.
- Access Your Account – After you log in, the system will direct you to your GST Login portal. Here, you can access many features and services on the GST Login portal. These tasks include filing returns. They also include making payments. And updating details.
That’s it! You’ve logged in to the GST portal. Now, you can do your GST tasks online. Remember to log out of your GST Login Portal account. Do this after you finish your activities to stay secure.
Accessing the GST portal is quick and easy. It empowers businesses to manage their taxes well.
Why do businesses need to file GST regularly on the GST Login Portal?
GST, known as Goods and Services Tax, plays an important role in the Indian Tax system. Let’s understand in detail why it is important for businesses to file GST.
Filing GST ensures compliance with the law. In India, businesses must register for GST if they have a certain turnover.
Once registered, they must file GST returns timely. These include their sales and purchases. They are doing so as the law requires.
Filing GST allows businesses to claim input tax credits. The input tax credit is the tax paid on purchases.
You can subtract it from the tax collected on sales. Filling GST returns on time helps businesses. They can then claim input tax credit, which lowers their tax. It eases the tax burden on businesses.
By filing GST returns, that is how they also make taxes transparent. This transparency helps tax authorities. It lets them verify tax payment accuracy and stop tax evasion., it contributes to a fair tax system.
Businesses register for GST. They follow tax rules to get benefits. They also get opportunities. These include government contracts, loans, and subsidies.
GST replaced the old tax structure. Fragmented before, it now unifies. This makes it easier for businesses in many states to comply. It also removes interstate barriers. This makes operations smoother. It also makes the company more competitive.
In conclusion, businesses must file GST. businesses must do it to follow the law. They claim tax credits and promote transparency.
They also access benefits and aid trade between states.
It helps businesses and the whole economy to grow. So, Businesses must fulfill their GST obligations.
What if we missed filling GST on the GST Login Portal?

Missing the deadline to file GST returns can put you in a legal situation.
It can have serious consequences. Let’s explore what happens if you miss filing your GST in simple terms.
First, missing the GST deadline can lead to penalties. The government imposes late fees. They are for filing GST returns late.
These penalties can build up. They add to the financial burden on businesses over time.
Also, not filing GST can lead to legal trouble. The government may sue businesses.
They fail to file their GST returns. This can include fines and prosecution. It can also mean suspension or cancellation. It affects GST registration.
Businesses may face difficulties. In case, if you don’t file GST returns on time. This can hurt their ability to claim input tax credits.
That can hurt their cash flow and profitability. It can also lead to disruptions in supply chains. It can harm business relationships.
Also, not filing GST can harm your business. It can harm your reputation. They may lose trust in your business.
This can happen if you fail to pay taxes. This can harm your brand for a long time. It will hurt your image and credibility in the market.
Also, missing GST filing deadlines can bar you from access. It can block you from government schemes. It can also cut your benefits.
By missing GST filings. You may miss valuable opportunities. These are for financial help and support.
They face fines and legal action. They also face disruptions. These cause damage to reputation and loss of benefits.
So, businesses must focus on filing GST on time. This is to avoid these bad results. You must set up systems.
You must do this to follow GST rules. This is crucial for the success of your business.
How often must someone file GST? Is it monthly, quarterly, or yearly?

GST is an important tax regime in India. Businesses need to follow it. But how often do businesses need to file GST returns? Let’s understand the process in an easy way.
To file the GST depends on the type of business and its turnover and accordingly you are required to file the GST (Monthly, Quarterly, Annually). Most companies need to file GST returns monthly. This means businesses must file their GST returns every month. You should do this regularly within each month. They need to provide certain pieces of information. They have to show their sales and purchases made during that period.
There are some exceptions to this rule.
This is instead of monthly. This relieves them from monthly filing. It allows them to file GST returns once every three months.
Businesses must file often. If they don’t, they will face penalties and legal trouble. They must follow the prescribed frequency. Missing the GST filing deadline can result in late fees.
The government imposes these penalties. Businesses should ensure to file their GST returns on time.
This is true whether it’s monthly, quarterly, or yearly. The timing depends on their turnover. It also depends on their registration status.
In conclusion, the frequency of GST filing varies. It depends on the turnover and registration of the business. Companies must file GST returns every month.
However, some of them may choose to do it quarterly. It is necessary to file these returns on time because failure to do so attracts penalties and makes businesses non-compliant with GST rules.
Filing your GSTs on time that’s what matters for business continuity and sustainability. They can also avoid any unnecessary problems or debts.
Which item does GST exclude?

GST, or Goods and Services Tax, applies to most goods and services in India. It is a comprehensive tax. GST excludes certain items. Let’s explore which items fall under this category in simple terms.
One category of items excluded from GST is essential food items. Basic food products are exempt from GST. These include fruits.
They also include vegetables. They have grains and fresh meats. This exemption aims to keep food affordable.
Healthcare services are also excluded. They are a type of item not taxed under the GST. Doctors, hospitals, and clinics provide medical services. These services are not subject to GST.
The same is true for vital healthcare items. This includes medicines and medical devices, which are exempted from the GST. This is aimed at ensuring that the prices are reasonable for patients as well as making them affordable.
Moreover, educational services are exempt from GST such as school/university education or coaching classes. It has educational materials. The government aims to promote access to good education for all.
Also, GST excludes some farm products. It also excludes inputs. This includes farmland. It also includes animals and machinery. Excluding these items from taxation helps support the farm sector and ensures food security and rural livelihoods.
Besides, banking, insurance, and stock trading have no GST implications on their transactions thus maintaining a stable financial system.
The above-mentioned facts regarding exemptions in relation to G.S.T show its omission of certain goods so as to make them affordable, accessible, and run effectively by vital sectors like food, health care, education, and agriculture finances.
It also ensures they follow tax rules. By knowing which items are exempt from GST, businesses can make informed decisions. They can also avoid unnecessary tax liabilities.
How many items come under the GST?

GST is a comprehensive tax in India. It aims to streamline taxes. But how many items fall under the ambit of GST? Let’s go through the simple process and understand.
GST covers a wide range of goods and services across various sectors of the economy.
Under GST, nearly all goods and services fall into the category of taxable items. But a few are exempt. This means that the scope of GST is extensive and encompasses a vast array of items.
GST covers goods. These include electronics, clothing, autos, household items, and consumables.
Whether you’re purchasing a smartphone, a pair of shoes, or a packet of biscuits,
GST applies to these goods. Services like healthcare, education, transportation, and hospitality are also subject to GST. This includes professional services.
One of the key features of GST is its uniformity across the country. Before the GST, each state and union territories used to have their own tax system.
But now GST is a single tax system that applies in all states and union territories. It helps businesses now to manage taxes and run smoothly.
There are multiple tax slabs in GST as per the types of Goods and services. It starts from 0% (Exempt) to 5%, 18%, and 28%. Some items such as foods grains and healthcare types of products have lower GST rates at the same time on luxury items you need to pay higher GST rates.
There are some items where GST does not apply such as Fresh fruit, Vegetables, and whole grains and some essential medicines and educational services. It’s ensured they are affordable and accessible for consumers.
What is TCS?

Apart from GST, there are TCS (Tax Collected at Source). Let’s Understand what exactly TCS is and how it works.
TCS is a mechanism designed to track transactions. It ensures tax compliance, in e-commerce. It requires certain businesses to collect tax at the time of sale and remit it to the government. The goal behind TCS is to curb tax evasion and improve tax administration.
In practice, if you buy goods from an e-commerce platform, the seller may collect TCS from you at the time of the sale. This TCS amount is then deposited with the government. The e-commerce platform acts as a middleman. It collects tax for the government.
The TCS rate of TCS under the GST can vary and it is dependent on which types of transactions and parties are involved. For example, The TCS rate for selling goods can be different from the TCS rate for providing services. The rates may also vary for different transactions.
It’s important to note that not all transactions are subject to TCS. Certain exemptions and thresholds may apply. It depends on the seller’s turnover and registration status. TCS applies only to certain types of businesses. It affects those in e-commerce.
The purpose of TCS is not only to collect tax but also to ensure compliance with GST regulations. The government aims to create a more clear and accountable tax system by mandating TCS. It also reduces the tax gap.
It does this by catching transactions that may go unnoticed. Finally, the reason behind TCS in GST is to improve tax compliance. Mainly it’s focused on the e-commerce sector.
The employers whose nature of business is e-commerce must need to have knowledge of TCS. This will help employers to follow the GST rules and avoid penalties
What is CGST?

CGST is known as the Central Goods and Services Tax. GST is levied by the central government on the sale of goods and services within the same state. It is one of the three taxes in the GST system. The other two are SGST and IGST. The state government levies SGST. IGST applies to interstate transactions. The central government collects CGST.
The purpose of CGST is to combine many central taxes. These include Central Excise Duty, Service Tax, and Central Sales Tax. They are being combined into a single tax system.
At each stage of the supply chain, levies CGST on the value of goods and services. It goes from making to the final sale to the consumer. The rate of CGST varies. It depends on the type of goods or services.
One of the key features of CGST is its input tax credit mechanism. Under this rule, businesses can claim credit for the CGST paid on their purchases. They can use it against the CGST they collect on their sales.
This reduces the total tax and ensures that taxes are only on added value at each stage of the supply chain.
IGST is imposed on the transaction that transports goods and services across borders. In a simple word, CGST is tax that is imposed by the Central government on the supply of goods and services within a state.
What is SGST?
SGST (State Goods and Services Tax) plays an important role in the GST system. Let’s understand in this article what exactly SGST means, how it works, and who needs to pay SGST.
SGST is a tax that is imposed by the state government on the supply of goods and services within a state.
It is one of the three taxes in the GST system. The others are CGST and IGST. The central government collects CGST. But state governments run and collect SGST.
SGST’s main goal is to ensure that states have the freedom to tax transactions in their borders. They can also collect the taxes. This allows states to make money. They use it to fund development and public services.
As CGST does, SGST imposes taxes on the value of goods and services at every stage of the supply chain. Each state government sets the SGST rate. It may vary by state. However, it is usually set at the same rate as CGST to maintain uniformity in tax rates within a state.
SGST has a key feature: its input tax credit. It lets businesses claim credit for the SGST paid on their purchases. They can claim it against the SGST they collect on their sales. This reduces the tax burden on businesses. It ensures that taxes are only on added value at each stage of the supply chain.
SGST applies only to intra-state transactions. These are transactions within the same state. IGST levies for transactions that cross state borders. Instead of the government levying SGST and CGST, it levies them.
In summary, SGST is a state-level tax levied on the supply of goods and services within a state. It lets states tax transactions within their borders. It is vital for making money and funding development.
What is IGST?

IGST is one of the important categories that come under the GST system. In this article, we will get to know more in detail about IGST what IGST is, and how is it different from CGST and SGST.
The IGST tax is applied by the Central Government. It is a country-specific regulation that refers to the sale of merchandise and services. They must move across state borders. IGST is different from CGST and SGST.
The central government collects CGST, and the state government collects SGST. However, the central government administers IGST.
When one state supplies goods or services to another, the transaction incurs IGST. The rate of IGST is usually equal to the combined rate of CGST and SGST applicable in the destination state.
The main features of IGST are its destination-based taxation principles. This means that the amount collected under the IGST tax system directly goes to the destination state’s account. When a consumer avails any services or buys goods at this location that ensures where consumption is happening gets its fair share of taxes.
There is one more aspect of IGST which is input tax credit mechanisms, like SGST and CGST. Business owners can claim credit for the IGST that is paid on their interstate purchases. This can be used against the IGST that they collect on their interstate sales.
All about IGST, IGST is a central tax that is imposed on interstate transactions of goods and services. It helps in trading between the states. One of the main benefits of IGST is that the tax rates are the same everywhere and it prevents double taxation. Any businesses that are doing transactions across state borders must understand about the IGST
What is UTGST?

UTGST is a tax that applies in union territories, and it is imposed by the Central Government. It applies on the supply of goods and services in the Union Territories of India. Like the CGST, the central government administers and collects it. But it applies to the Union Territories, not the states.
UTGST’s main goal is to ensure that Union Territories have the freedom to levy taxes. They can collect taxes on transactions in the territory. This lets Union Territories raise money. They use it to fund development and public services in their area.
UTGST operates on the same principles as CGST and SGST. It has similar input tax credit rules and compliance requirements. Businesses in Union Territories must register for UTGST. They must also file returns. The returns should detail their transactions within the territory.
One of the key features of UTGST is its role in ensuring tax uniformity. It does so across Union Territories. Union Territories do not have their own legislatures. They cannot enact separate tax laws, unlike states.
UTGST provides a standard tax framework for Union Territories. It ensures consistent and simple tax administration.
Like SGST, UTGST applies only to intra-territory transactions. In brief, UTGST is a tax that is applied by the central. Tax authority imposed the tax on supplying the goods and services. It is applied within the Union Territories.
A Union Territories can collect taxes on transactions within their borders. This tax helps in developing the union territories. Those who are doing business in Union territories must know all about UTGST to avoid any penalties and breaking any tax rules.
How does the GST Login Portal work?

GST (Goods and Services Tax) is type of tax that exist in India. The purpose of launching this GST Login Portal tax system is to streamline the tax process for taxpayers in India. In this article, we are going to learn about how GST works and what are the main key points of the GST.
GST is a tax that applies to the supply of goods and services. GST has replaced many other different types of taxes, now you just need to pay one tax called GST.
The GST is imposed by the Central and State governments. The reason behind implementing GST is to avoid all other indirect taxes that are used to create confusion.
Under GST, the government categorizes goods and services into different tax slabs. Their nature and importance determine this. These tax slabs range from 0% (exempt) to 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. Some key items may have lower GST rates. However, luxury items may have higher rates.
GST operates on a dual model, consisting of central and state components. The central part includes CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax). The central government levies it. The state part includes SGST (State Goods and Services Tax). The state governments levy it.
GST operates on self-assessment. Taxpayers must calculate and file their tax returns on time.
What are the benefits of the GST Login Portal?

GST, or Goods and Services Tax, has changed taxes system in India. It all happened just because of the implementation of GST. But what are the benefits of GST and how does it impact businesses and consumers? Let’s understand the benefits of GST in simple words.
GST has played an important role in streamlining the tax structure in India. Its main benefit is that after the GST implementation, we do not need to pay multiple indirect taxes imposed by the state and central government. GST is a single and unified tax system.
The previous tax regime-imposed tax on taxes. This was creating a cascading effect known as tax-on-taxes. It allows the business to claim tax credits on the purchase. This effectively ensures that the tax is paid depending on the value added at every stage of the supply chain for goods.
The economist believes that GST can boost the Indian economy’s growth. This will happen by promoting trade, investment, and consumption. GST streamlines taxes.
Transparency and Compliance: GST promotes transparency and compliance in the tax system. You can register, file, and pay taxes online through the GSTN portal. This lets taxpayers follow GST regulations. This reduces tax evasion and enhances tax administration efficiency.
Consumers enjoy GST. It lowers the tax on goods and services. The elimination of many taxes will end the cascading effect. We expect prices of goods and services to drop. This will make them cheaper for consumers.
GST has many benefits. These include a simple tax structure and the end of the cascading effect. GST also brings uniform tax rates and boosts growth. It adds transparency, aids compliance, and helps consumers.
These advantages help businesses and consumers understand the GST landscape well. They can use them to grow and prosper together.
What are the different GST laws and regulations?
Laws govern GST, or Goods and Services Tax. They determine how to install and administer it in India. Let’s delve into the GST laws and regulations. We want to understand how they govern taxes.
The CGST Act is the Central Goods and Services Tax Act. The central government enacted it. It governs the levy and collection of CGST on the supply of goods and services within a state.
The central government enacted the IGST Act. It governs the levy and collection of IGST. The tax is on interstate transactions of goods and services. It outlines the rules for the place of supply, tax rates, and tax revenue distribution. It explains the division of revenue between the center and states.
The UTGST Act is a law enacted by the central government. It dictates the levy and collection of UTGST. This applies to the supply of goods and services within Union Territories. It operates under the SGST Act but applies to Union Territories.
The GST Compensation Cess Act is about the Goods and Services Tax Cess Act. It compensates states. The central government made it. It covers the levy and collection of compensation cess on certain goods and services.
The government makes GST rules under the GST Acts. They provide detailed guidelines for GST administration. You can find about registration, invoicing, input tax credits, return filing, and audits in the guidelines of the GST.
What are the GST rates for different goods and services?
GST, Goods and services tax is a tax system in India. It is applicable to a wide range of goods and services. But what exactly is the rate of GST on goods and services? Let’s understand this in a simple and easy way.
There are five types of tax categories where the first one starts from 0%, 5%, 18% and 28%. Each tax category will apply to the goods and services. Let’s have a look below at which item applies which tax slab.
0% GST applies on some essential items. Fresh fruits, grains, vegetables, milk, eggs, and healthcare services are the ones where 0% GST applies. These items are more affordable as GST does not apply to these items.
5% GST applies on items such as packaged food, coffee, and tea. Under certain conditions, 5% GST applies on medicines and affordable housing. It makes sure that consumers can avail the essential items at affordable prices.
12% GST applies to processed food, mobile phones, apparel, computers, and construction. This 12% GST rate helps in building a balance between revenue generation and consumers.
18% GST applies to items like restaurants, telecom, and financial services. It also applies to footwear and furniture. This rate applies to goods and services. They do not consider them essential or luxury.
28% GST rate applies to luxury items and goods such as high-end electronics, autos, cosmetics, and sodas.
It is good to have a broad knowledge of GST as there are certain goods and services that the combination of GST can attract. For example, gold attracts a 3% GST rate along with making a charge rate of 5% GST.
Knowing the GST rates helps businesses. It lets them ensure accurate invoicing and tax compliance. Consumers can use it to make budget-conscious shopping choices.
How did GST implementation affect businesses?
GST (Goods and Services Tax) changed taxation in India. It marked a big shift. It impacted all types of businesses and sectors. Let’s have a look at how GST implementation impacted the country.
GST made tax simple. It’s replaced all types of indirect taxes. There is only one tax system which is GST. After, the GST implementation businesses can focus on their growth instead of worrying about filing multiple types of taxes.
ITC (Input Tax Credit) Introduced by the GST helps businesses claim credit for the GST that is paid on their purchases. They can claim it against the GST they collect on their sales. This mechanism reduced the cascading effect of taxes.
It ensured that taxes were only on the value added at each stage of the supply chain. Businesses could cut their tax and manage cash flow by using ITC well.
Interstate trade improved with the GST. It reduced barriers. The IGST simplified the tax on interstate transactions. It made it easier for businesses to move goods across state borders. This made trade easier. It improved market access for businesses in many states.
Implementing and making businesses obey this GST regime was very challenging. The main purpose of implementing GST was to make tax simple. But at starting of the launch, it was a problem for businesses, especially for small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
Understanding the new tax process for the businesses was quite challenging. Businesses were prepared and were not aware of how to register for GST, how to get GST numbers, file returns,s, etc.
Many businesses had to invest in training. They also needed technology upgrades to follow GST regulations. The transition to GST had costs for businesses. These included restructuring supply chains, updating accounting systems, and revising pricing.
What were the challenges during the transition to GST?

GST was the biggest change in the tax system in India ever. It was implemented just to make the tax system simple and drive the growth of the Indian economy. But it was not as easy as it seemed. There were many issues the government has faced to implement this. Let’s explore this in detail.
GST rules was complex: one of the main challenges in the transition was to understand its rules. However, Businesses adapt to the new tax regime. They get training about online registration, filing returns, invoicing, etc. It took time to get familiar with GST.
Technologically ready: To apply GST smoothly in the market, adopting digital technology was necessary. It helps in tax compliance and reporting.
The businesses that are working from rural and remote areas face challenges. They were not properly ready to move to digital platforms. This was due to limits in infrastructure and a lack of awareness. This posed hurdles in timely compliance with GST regulations.
Classifying and taxing goods under GST posed challenges for businesses. This was especially true for those in sectors with complex product lines. Finding the right tax rate for goods and services needs careful analysis.
It also needed interpretation of GST laws. This caused confusion and uncertainty among businesses.
Businesses were struggling during the transition as the GST regime was completely unfamiliar to all the business owners. Despite these challenges, business owners show interest in GST and help achieve a big milestone in India’s tax reform.
The purpose of implementing GST is to make more transparency in tax, uniform, and efficient. now in 2024, almost every business owner obeys the GST rules and works as per the GST guidelines.
What are the differences between pre-GST and post-GST regimes?

Before the Goods and Services Tax (GST) taxes were confusing.
Before the GST there were many types of taxes that existed in India like Value-added tax (VAT), and excise duty. Managing these many taxes was hard for businesses.
It led to an extra burden and more work. GST replaced many different taxes with a single tax called GST.
Now, for businesses it is quite easy to manage the tax system with a lower burden and less manpower.
Now, when GST is there, we have seen significant changes in tax rate structure. It puts goods and services into different tax slabs. These ranged from 0% to 28%. These equal tax rates made taxes consistent and clear. They helped trade between states and reduced tax barriers.
A key difference between the pre-GST and post-GST regimes is the ITC mechanism.
With GST, it is very easy to claim credit for the GST paid on your purchases. You can use it against the GST collected on your sales.
In summary, the shift from the pre-GST to the post-GST regime made big changes to India’s taxes.
The changes included a simpler tax structure. They kept the same tax rates and the input tax credit. They also made interstate trade easier and digital compliance simpler. These differences affected businesses. They made business easier and fostered growth.
GST FAQ’s
- CGST: Central Goods and Services Tax, collected by the Central Government on an intra-state sale.
- SGST: State Goods and Services Tax, collected by the State Government on an intra-state sale.
- IGST: Integrated Goods and Services Tax, this tax is collected by the Central Government for inter-state sales.
- Making Tax Structure Easy: Consolidated all the other Indirect Taxes into one tax.
- Elimination of Cascading Effect: Input tax credit is available across the supply chain, reducing the tax burden on businesses.
- Making Taxes transparent: Uniform tax rates and structures improve compliance and reduce tax evasion.
- Boost to Economy: Simplifies the tax regime, encouraging businesses and economic growth.